Ambident Reactivity of the Cyanate Anion
28-Mar-2008
Chem. Eur. J., 2008, 14, 3866-68 published on 28.03.2008
Chem. Eur. J.
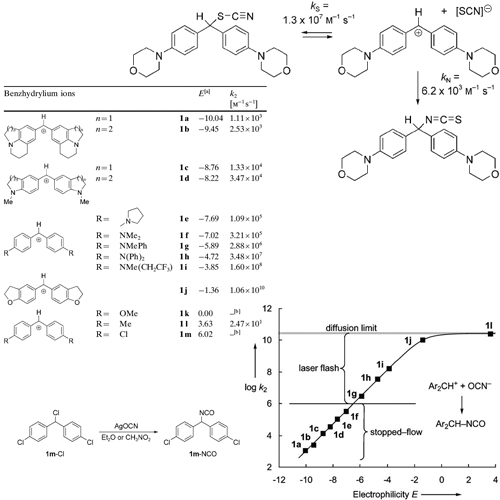
The cyanate anion is an ambident nucleophile, which may react with electrophiles either at the oxygen terminus to yield alkyl cyanates or at the nitrogen terminus to yield isocyanates. Because the charge density is higher at the more electronegativeoxygen center while the larger HOMO coefficient is at nitrogen, the concept of charge and orbital control predicts hard electrophiles to attack at the oxygen side and soft electrophiles to attack at the nitrogen. It was, therefore, expected that alkyl cyanates should be formed in nucleophilic substitution reactions with SN1 character while alkyl isocyanates should be formed in nucleophilic substitution reactions with SN2 character.